SMS Based Controlling Different Industrial Machines Using GSM Mobile and microcontroller 8051
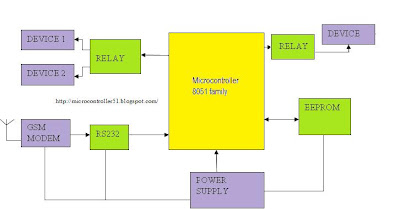
This project (interfacing mobile phone with microcontroller 8051 for machines control through SMS) has many important other applications and can be used to control Switch ON or OFF any machines at far off places using a gsm modem by sending sms through the communication between the mobile and the embedded devices (microcontroller 8051).This remote control of appliances is possible through Embedded Systems. The use of “Embedded System in Communication” has given rise to many interesting applications that ensures comfort and safety to human life. The microcontroller is interfaced with GSM Modem in mobile phone via MAX232 level convertor. The microcontroller project is designed to allow easy use of a mobile phone to control appliances or machines at any far location may be in industry or at home. Using a mobile phone the development of the control system will be carried out using SMS. This will communicate with another mobile phone, which in turn controls the devices attached to microcontroller modules. When the action has been carried out then a response is sent to the user. The use of mobile phones to remotely control an appliance control system. The microcontroller would then control the device based on the information given to it.
The devices are connected to the 8051 microcontroller using relays and optocouplers. These relay are controlled through software to switch ON or OFF the device as required. For every message received to microcontroller through mobile phone in form of SMS, the controller will check for the valid and pre-define formate. If the message is correct the controller will perform the operation.
The hardware board contains microcontroller AT89c52 at the heart of the system. The microcontroller is interfaced with GSM Modem of mobile phone via MAX232 level convertor. It is used to convert RS232 voltage levels to TTL voltage levels.
The AT89C52 is a low-power, high-performance CMOS 8-bit microcomputer with 8K bytes of Flash programmable and erasable read only memory (PEROM). The device is compatible with the industry-standard 80C51 and 80C52 instruction set and pin out. The on-chip Flash allows the program memory to be reprogrammed in-system or by a conventional non-volatile memory programmer which provides a highly-flexible and cost-effective solution to many embedded control applications.A GSM modem is a wireless modem that works with a GSM wireless network. A wireless modem behaves like a dial-up modem. The main difference between them is that a dial-up modem sends and receives data through a fixed telephone line while a wireless modem sends and receives data through radio waves. Like a GSM mobile phone, a GSM modem requires a SIM card from a wireless carrier in order to operate.
Generally, computers use AT commands to control modems. Reading of message from the SIM card inserted into the modem is done by sending the appropriate AT command to the modem.
The MAX232 is a dual driver/receiver that includes a capacitive voltage generator to supply EIA-232 voltage levels from a single 5-V supply. Each receiver converts EIA- 232 inputs to 5-V TTL/CMOS levels. Each driver converts TTL/CMOS input levels into EIA-232 levels.
GSM Modem, which works at RS-232 voltage levels, logic 1 varies from -3 to -15 volts and logic 0 from +3 to +15 volts. The microcontroller which works on TTL logic levels, logic 1 is +5 volts and logic 0 is 0 volts. Therefore to interface the two we use a MAX 232 driver IC.
AT-Command set
The following section describes the AT-Command set. The commands can be tried out by connecting a GSM modem to one of the PC’s COM ports. Type in the test-command, adding CR + LF (Carriage return + Line feed = \r\n) before executing. Table gives an overview of the implemented AT-Commands in this application. The use of the commands is described in the later sections.
AT-Command set overview
The AT Command | Description of Commands |
AT | Check if serial interface and GSM modem is working. |
ATE0 | Turn echo off, less traffic on serial line. |
AT+CNMI | Display of new incoming SMS. |
AT+CPMS | Selection of SMS memory. |
AT+CMGF | SMS string format, how they are compressed. |
AT+CMGR | Read new message from a given memory location. |
AT+CMGS | Send message to a given recipient. |
AT+CMGD | Delete message. |
GSM Modem is used to receive message from the authorized user. This GSM modem requires a SIM card from a wireless carrier in order to operate. This SIM number is contact number of the receiving section.
, the AT89S52 is designed with static logic for operation down to zero frequency and supports two software selectable power saving modes. The Idle Mode stops the CPU while allowing the RAM, timer/counters, serial port, and interrupt system to continue functioning. The Power-down mode saves the RAM con-tents but freezes the oscillator, disabling all other chip functions until the next interrupt. In this project MODEM is communication with the microcontroller through serial port, the microcontroller will send the commands to the modem through RS 232.and the data is read through serial port therefore to make compatible computer serial port with microcontroller serial port we are using the RS 232 converter.A GSM network is composed of several functional entities, whose functions and interfaces are specified. Figure 1 shows the layout of a generic GSM network. The GSM network can be divided into three broad parts. The Mobile Station is carried by the subscriber. The Base Station Subsystem controls the radio link with the Mobile Station. The Network Subsystem, the main part of which is the Mobile services Switching Center (MSC), performs the switching of calls between the mobile users, and between mobile and fixed network users. The MSC also handles the mobility management operations. Not shown is the Operations and Maintenance Center, which oversees the proper operation and setup of the network. The Mobile Station and the Base Station Subsystem communicate across the Um interface, also known as the air interface or radio link. 8051 provides a transmit channel and a receive channel of serial communication. The transmit data pin (TXD) is specified at P3.1, and the receive data pin (RXD) is at P3.0. All modes are controlled through SCON, the Serial control register. The timers are controlled using TMOD, the Timer mode register, and TCON, the Timer control register.






Where can i get the circuit diagram and code
ReplyDelete